When selecting wire ropes, two perspectives must be considered: the application requirements and the wire rope characteristics.There is no "universal wire rope" that suits all applications. This is why wire ropes come in so many structural types—to best meet the needs of various uses.
1)Selecting Wire Ropes from the Application Perspective
The primary task of a crane is to lift and move loads, which requires hoist ropes. In addition to this critical "lifting function," there are many other applications, such as:
a) Luffing ropes for adjusting the boom;
b) Trolley ropes used on tower cranes, ship unloaders, and container gantry cranes to move cargo;
c) Stay ropes for securing the boom or other crane structures;
d) Other specialized uses.
2)Selecting Wire Ropes Based on Rope Characteristics
Wire ropes for crane applications can be categorized into three types based on their construction:
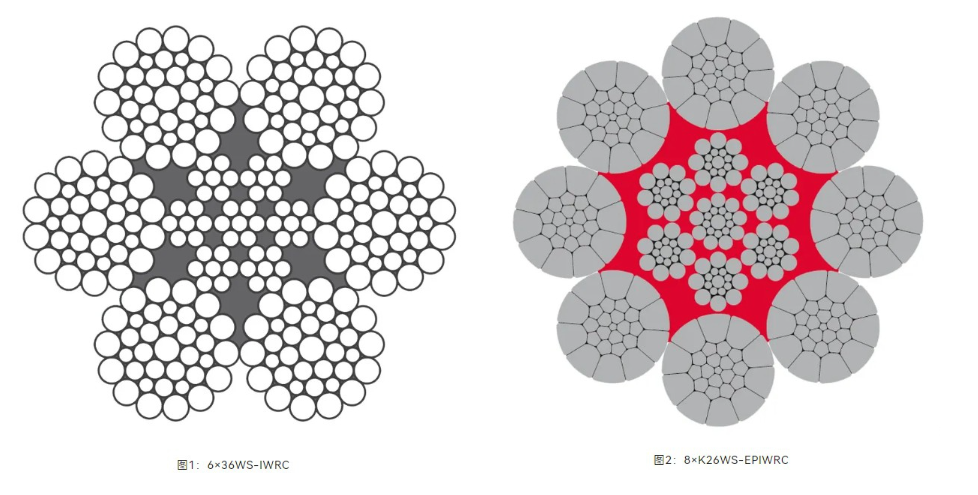
a) Non-rotation-resistant ropes, such as 6-strand or 8-strand single-layer ropes (Figures 1 & 2).
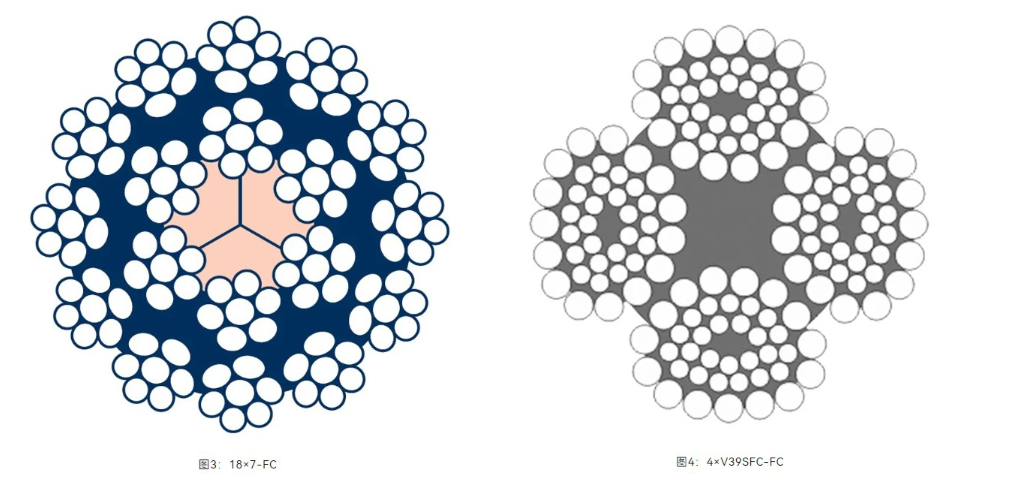
b) Semi-rotation-resistant wire ropes, typically referring to two-layer strand and 4V-type wire ropes, such as 18×7 and 4V structural wire ropes (Figures 3 & 4).
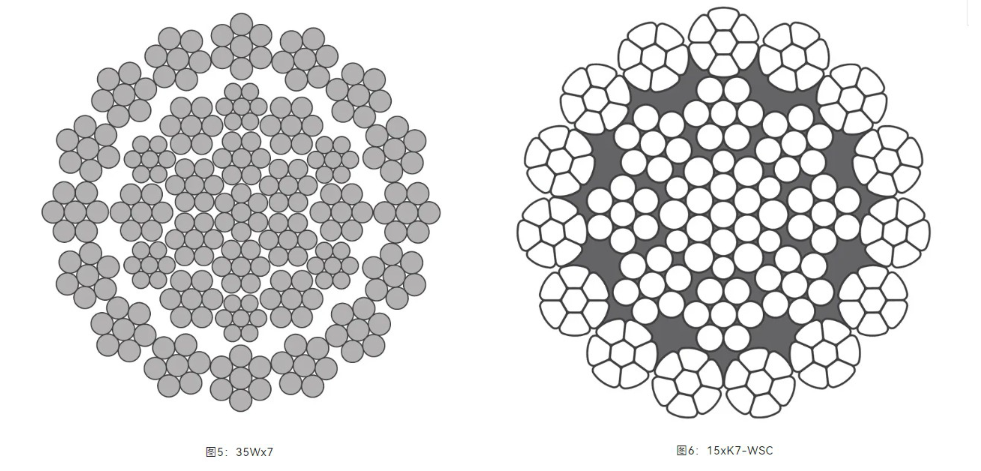
c) Rotation-resistant wire ropes, commonly referred to as non-rotating ropes or multi-layer strand ropes (typically three-layer), such as 35W×(K)7, 40W×(K)7, and 15×(K)7 (Figures 5 & 6).
2. Selection of Wire Ropes for Crane Applications
Basic Guidelines for Selecting Hoist Ropes in All Crane Applications:For both main hoist ropes and auxiliary hoist ropes, rotation-resistant wire ropes must be used if the following conditions are met:
1) Single-Rope Lifting of Unguided Loads (Figure 7),
2) High-Height Lifting Operations (Figure 8).

Only rotation-resistant wire ropes can provide load stability, ensuring the load does not rotate or rotates minimally. When fixed to crane structures, rotation-resistant wire ropes transfer little to no torque to the attachment points. Thus, they ensure safe lifting operations and secure crane performance.
3. Selection of Wire Ropes for Crane Applications (Part 2)
As with all rules, there are exceptions under certain circumstances:
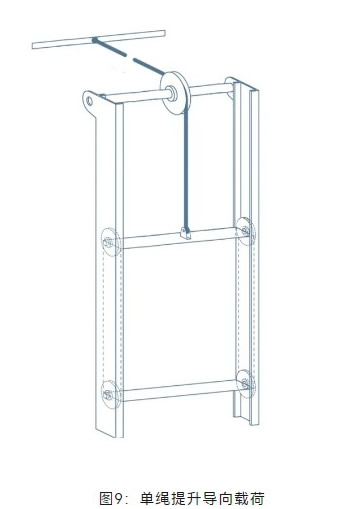
1) In applications with guided loads, non-rotation-resistant wire ropes may also be used, as the load-guiding frame prevents torque generation from load rotation (Figure 9).
2) When lifting unguided loads, non-rotation-resistant wire ropes may also be used if designed in pairs with left-lay and right-lay rope combinations (Figures 10 and 11).

The second configuration also provides rotational stability, resulting in minimal rotational tendency of the load. This is achieved because the generated torques under load are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, thereby creating torque balance.
4. Other Applications of Wire Ropes in Cranes
Non-rotation-resistant wire ropes generally exhibit higher bending cycle performance compared to rotation-resistant or semi-rotation-resistant wire ropes. However, they impose torque on connected end fittings under load. Therefore, non-rotation-resistant wire ropes may only be used if the rope ends are permanently secured against twisting.
Non-rotation-resistant wire ropes are always the correct choice when rotation resistance is not required in the application. This applies to many wire rope uses, such as luffing ropes, trolley ropes, boom ropes, etc.

